When you're placing a manufactured home in Maine, understanding wind zones isn't optional. These classifications determine how your home gets built, what anchoring system it needs, and whether it can handle the weather that hits the Pine Tree State throughout the year.
Maine wind zones are set by the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) to make sure manufactured homes can withstand regional wind speeds. The zones directly affect building standards, safety requirements, and insurance costs.
What Are Wind Zones?
Wind zones measure the wind pressure a manufactured home must handle based on location. HUD created three classifications in 1976 as part of the Manufactured Home Construction and Safety Standards (the HUD Code):
Zone 1: Homes must resist winds up to 70 mph
Zone 2: Homes must resist winds up to 100 mph
Zone 3: Homes must resist winds up to 110 mph
Each zone requires increasingly stronger construction. Mobile home wind zones affect every structural decision, from roof design to wall anchoring. You can't build a home for calm conditions and expect it to survive storm-prone areas.
Related: What To Know About Windzones & Manufactured Homes
.png)
Maine's Wind Zone Breakdown
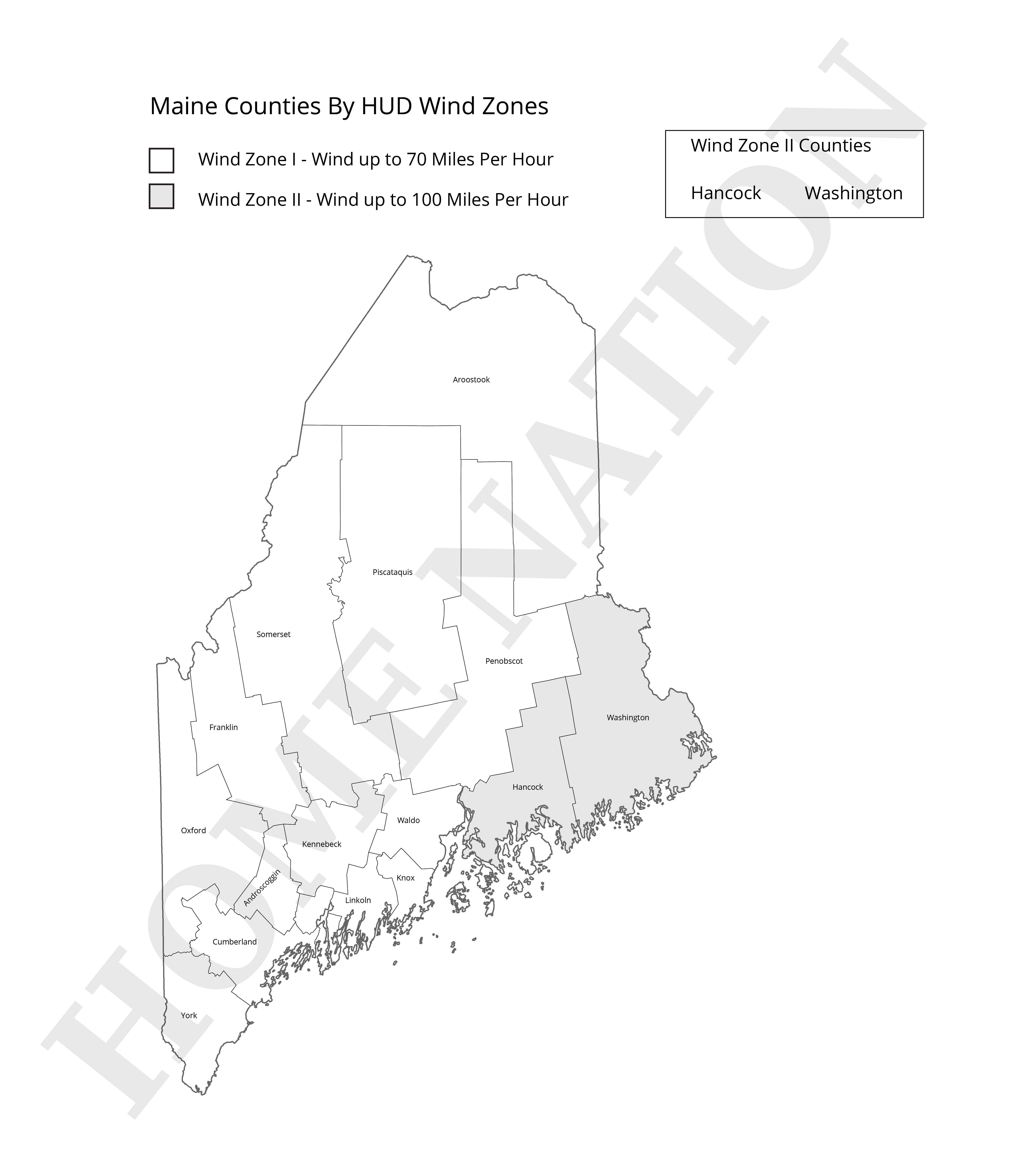
Most of Maine sits in Wind Zone 1. This covers interior counties like Aroostook, Piscataquis, Somerset, and Penobscot. Homes here handle winds up to 70 mph, which works for areas protected from direct coastal exposure.
Wind zone 1 counties:
Androscoggin Aroostook Cumberland Franklin Kennebec Knox Lincoln Oxford Penobscot Piscataquis Sagadahoc Somerset Waldo York
Coastal regions of Maine fall into Wind Zone 2. This includes portions of York, Cumberland, Sagadahoc, Lincoln, Knox, Hancock, and Washington counties. These areas face stronger winds, particularly during nor'easters and occasional tropical systems. Homes in Zone 2 must withstand winds up to 100 mph, similar to the requirements for hurricane-proof modular homes in other coastal states.
Wind zone 2 counties:
Hancock Washington
Maine doesn't have any Wind Zone 3 areas. The state's northern latitude and coastal geography keep it out of the highest-risk hurricane zones that require 110 mph resistance.
Why Maine's Weather Patterns Matter
Maine experiences several weather systems that affect your home's wind speed zone requirements. The coast gets hit by nor'easters during fall and winter, bringing sustained winds and coastal flooding. While tropical systems rarely reach Maine at full strength, the state occasionally sees weakened hurricanes or tropical storms between August and October. Unlike climate-threatened states farther south, Maine faces fewer direct hurricane impacts.
The Gulf of Maine's cold water typically weakens tropical systems as they move north. However, when these storms combine with frontal systems, they can still deliver damaging winds to coastal areas.
Maine Wind Zones and Building Standards
Maine wind zones determine how homes get constructed. Zone 2 coastal homes require reinforced connections between roof and wall framing, stronger anchoring systems to prevent uplift, and wall sheathing at closer intervals. This focus on building resilience applies to manufactured homes just as it does to hurricane-proof site-built homes.
The difference matters for safety and compliance. You can't place a Zone 1 home in a Zone 2 location. HUD prohibits manufacturers from installing lower-rated homes in higher wind zones. However, you can place a Zone 2 home in a Zone 1 area.
Related: Find The Best Hurricane Proof House Plans Of The Year

How to Verify Your Home's Wind Zone
Every manufactured home has a HUD data plate, usually in a kitchen cabinet, bedroom closet, or near the electrical panel. This plate lists your home's wind zone rating along with thermal and roof load information.
Can't find your data plate? You can request a replacement from the Institute for Building Technology and Safety. Before buying land or moving a home, contact your county building department to confirm the wind zone for your location.
Maine Wind Zone Mobile Homes
If you're shopping for a manufactured home in Maine, you need one that matches your location's requirements. Coastal buyers need Zone 2 certification, while interior residents can choose Zone 1 homes. Home Nation offers manufactured homes built to meet HUD wind zone standards for every region.
Whether you're ready to get preapproved for a new home or want to sell your current home, understanding Maine wind zones helps you make smart decisions. The right wind zone rating protects your investment and keeps your family safe during Maine's toughest weather.





