Mobile homes often get a bad rap in media of all types; from country songs to movies. Most of the time they depict these homes as easily demolished. The truth is far from this. Most often, mobile homes that see the most destruction are simply in wind zones they aren't meant for.
Understanding your state's wind zone classification is essential for safety, legal compliance, and protecting your investment. How do you know if you are setting your home on land in an approved wind zone; especially if you don't even know what wind zones are? Thankfully, there are ways to determine this information and ensure that you purchase a home and set it up with ease of mind.
Wind zones were established in 1976 as part of the HUD Manufactured Home Construction and Safety Standards (also known as the HUD Code) to ensure that every manufactured home is built to withstand the wind conditions specific to its location. This isn't just about building codes; it's about your safety and your home's structural integrity.
At Home Nation, we buy and sell mobile homes. Find out how you could sell or trade your home with us.
Why Wind Zones Matter for Mobile Home Buyers
Wind zone ratings determine how your manufactured home is designed, constructed, and anchored to the ground. Every component, from the roof trusses to the tie-down system, must meet specific engineering standards based on expected wind speeds in your area.
Here's what makes this critical: You cannot place a home built for Wind Zone 1 in an area designated as Wind Zone 2 or 3. Attempting to do so violates HUD regulations and puts residents at serious risk. The manufacturer is prohibited from installing a lower-rated home in a higher wind zone. However, a home built to higher standards (Zone 2 or Zone 3) can be placed in a lower zone.
Failure to account for these standards could delay the installation and approval of your new home, result in permit denials, void your warranty, and most importantly, compromise your safety during severe weather events.
Related Link: 10 Most Important Things You Should Know About Modular Homes
Understanding the Three Wind Zones
The United States is divided into three wind zones based on the fastest-mile wind speeds recorded in each region. These zones dictate the structural requirements for manufactured homes.
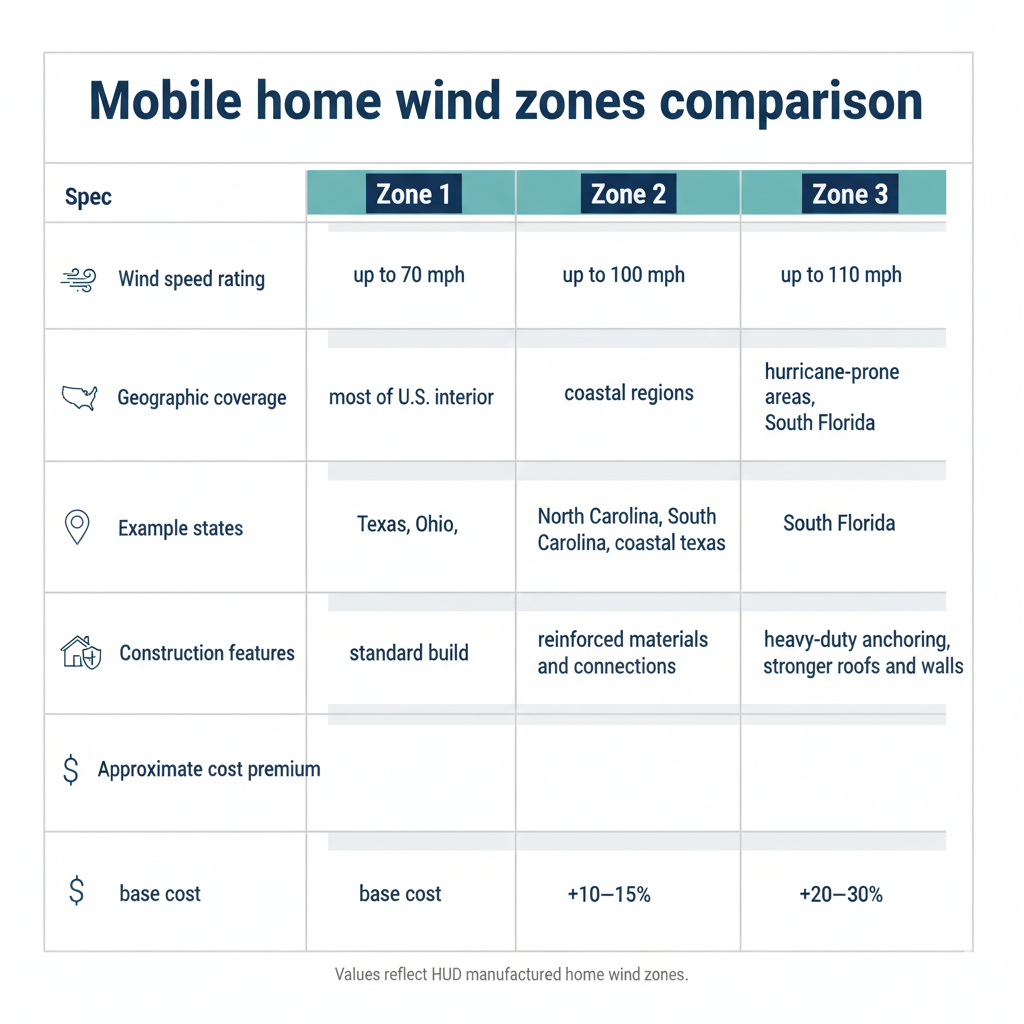
Wind Zone 1: Standard Wind Areas (Up to 70 MPH)
When manufacturers design a home, they must draft a design that can withstand specific wind loads. For Zone 1, the home must be able to withstand wind speed up to 70-mph. Zone 1 covers the largest geographic area of the United States, including most interior states and regions with lower wind exposure.
Zone 1 homes are designed for areas that experience typical seasonal winds, thunderstorms, and occasional severe weather but are not prone to hurricanes or sustained high-wind events.
Related: What Is Windzone 1 - States Included and More
Wind Zone 2: High Wind Areas (Up to 100 MPH)
As the zone numbers go up, so do the wind speeds. In Zone 2, homes are built to resist wind speeds up to 100 mph. Zone 2 covers hurricane-prone coastal regions and areas that experience stronger sustained winds. Most Zone 2 areas lie along the Atlantic Coast, Gulf Coast, and certain Pacific coastal regions.
Homes in Zone 2 require stronger roof systems, reinforced wall connections, enhanced anchoring systems, and upgraded fastening throughout the structure.
Related: What Is Windzone 2 - States Included and More
Wind Zone 3: Severe Wind Areas (Up to 110 MPH)
Finally, we come to Zone 3. This area sees the highest recorded wind speeds. As such, homes must include materials and designs that will help them resist these speeds. In Zone 3, homes must withstand wind speeds as high as 110 mph.
Zone 3 represents the most severe wind zones in the continental United States, including areas along the Florida Keys, portions of the South Florida coast, and other hurricane-vulnerable coastal zones. These homes require the most rigorous engineering standards and typically cost more due to enhanced structural requirements.
Related:What Is Windzone 3 - States Included and More
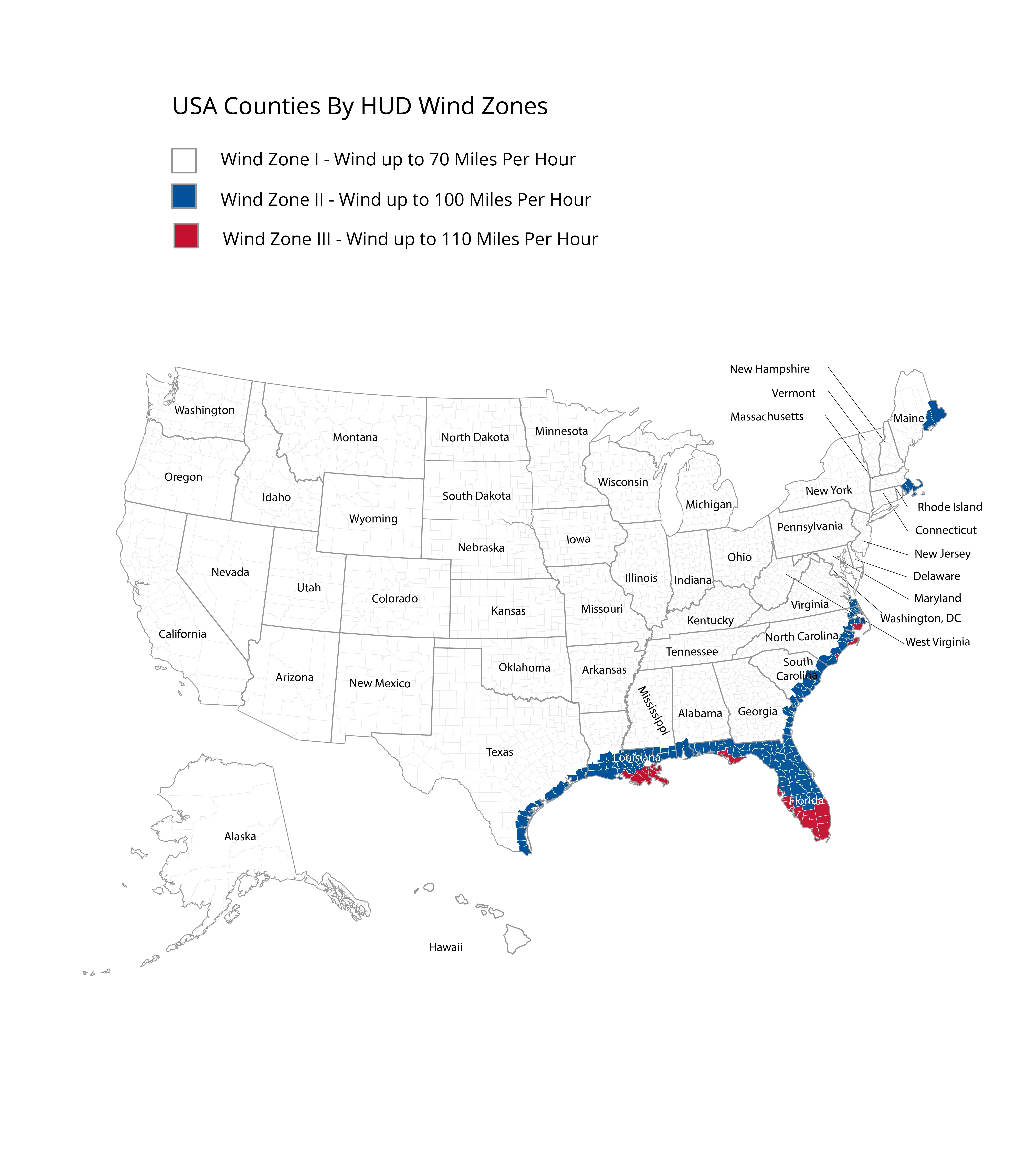
Wind Zones by State: Where Does Your State Fall?
Your state's wind zone classification depends on your specific location and proximity to coastal areas. Many states have multiple wind zones, with coastal counties in higher zones and interior regions in Zone 1.
Wind Zone 1 States (Interior/Low Wind Areas)
The majority of interior states fall primarily or entirely within Wind Zone 1, including:
-
Great Plains & Midwest: Montana, North Dakota, South Dakota, Nebraska, Kansas, Oklahoma (interior), Missouri, Iowa, Minnesota, Wisconsin, Illinois, Indiana, Ohio, Michigan (most areas)
-
Mountain West: Idaho, Wyoming, Utah, Colorado, New Mexico (interior), Nevada (most areas), Arizona (interior)
-
Interior South: Arkansas, Tennessee, Kentucky, West Virginia (most areas)
-
Northeast & Mid-Atlantic Interior: Vermont, New Hampshire (interior), Pennsylvania (interior), upstate New York
-
West: California (interior valleys), Oregon (interior), Washington (interior)
Wind Zone 2 States (Coastal/High Wind Areas)
Zone 2 encompasses coastal regions and hurricane-prone areas, including:
-
Atlantic Coast: Maine (coast), New Hampshire (coast), Massachusetts (coast), Rhode Island, Connecticut (coast), New York (Long Island, coastal areas), New Jersey (coast), Delaware (coast), Maryland (coast), Virginia (Tidewater/coastal), North Carolina (most coastal counties), South Carolina (most coastal counties)
-
Gulf Coast: Texas (coastal counties from Galveston to Brownsville), Louisiana (coastal parishes), Mississippi (coastal counties), Alabama (coastal counties including Mobile), Florida (approximately two-thirds of the state, excluding Zone 3 areas), Georgia (6 coastal counties: Chatham, Bryan, Liberty, McIntosh, Glynn, Camden)
-
Pacific Coast: Washington (coastal), Oregon (coastal), California (coastal regions)
-
U.S. Territories: Puerto Rico (portions), U.S. Virgin Islands (portions)
Wind Zone 3 States (Severe Wind/Hurricane Zones)
Zone 3 represents the most severe wind areas, limited to specific high-exposure coastal regions:
-
Florida: The Florida Keys, Miami-Dade County (coastal areas), Broward County (coastal areas), portions of Palm Beach County, Monroe County, and select Gulf Coast counties in Southwest Florida
-
Other Coastal Zones: Limited areas in South Carolina (barrier islands), North Carolina (Outer Banks exposed areas), Texas (extreme coastal exposure areas)
-
U.S. Territories: Portions of Puerto Rico, U.S. Virgin Islands (most areas), Guam, American Samoa
Important Note: Wind zones can vary by county and even by specific location within a county. Coastal areas within a state may be Zone 2 or 3, while interior counties are Zone 1. Always verify your exact location's wind zone classification with your local building department or county permitting office before purchasing a manufactured home.
Not sure about your area's wind zone? Contact Home Nation today and our team will help you identify your location's requirements and find the perfect home that meets all local wind zone standards.
Related Link: Mobile Home Skirting: Everything You Need to Know
How to Find Your Home's Wind Zone Rating
Knowing your home's wind zone will help you choose a mobile home that provides not only a roof over your head but also security and peace of mind. Clearly, you would not want to put a home designed for Zone 1 in an area that receives wind speeds like Zone 3. Now that you know where you want to live, how do you determine the zone your home was built for?

Check Your Home's HUD Data Plate
When dealing with your home's construction, it might seem easy to let the "professionals" deal with the details. However, knowledge is the most vital tool any person can utilize. As such, HUD stipulates that every home must have a data plate that includes zone maps for wind and other specifications. You can locate this in one of a few places: inside a kitchen cabinet, bedroom closet, or the electrical panel.
The HUD data plate is a paper document (usually white or yellow) permanently affixed to your home. It contains critical information including the manufacturer, serial number, model, and importantly, the wind zone classification your home was designed and certified for.
If you can't locate the data plate, don't worry. You can request a new one from the Institute for Building Technology and Safety or IBTS.
Contact Your Local Building Department
If you're planning to purchase land or move a manufactured home to a new location, contact your county building department or permitting office. They can tell you the wind zone classification for your specific address or parcel. This is especially important in states with multiple zones or near zone boundaries.
Mobile Homes by Wind Zone: Finding the Right Home for Your Area
At Home Nation, we offer manufactured homes built to meet all three wind zone classifications. Whether you're in the interior plains of Zone 1 or the coastal regions of Zone 2 and Zone 3, we can help you find a home that's engineered specifically for your location.
Wind Zone 1 Mobile Homes
Our Wind Zone 1 homes are perfect for buyers in interior states and low-wind areas. These homes meet all HUD standards for 70-mph wind resistance and offer excellent value for buyers in most of the continental United States. With the widest selection of floor plans, features, and customization options, Zone 1 homes provide maximum flexibility for your budget.
Wind Zone 2 Mobile Homes
For coastal buyers in hurricane-prone regions, our Wind Zone 2 homes provide the enhanced structural protection you need. These homes feature reinforced framing, upgraded tie-down systems, and stronger roof assemblies designed to handle 100-mph winds. While they represent a modest investment over Zone 1 homes, the added safety and compliance are essential for coastal living.
Wind Zone 3 Mobile Homes
Home Nation works with select manufacturers who build to Zone 3 specifications—the highest wind rating available for manufactured homes. These premium homes are engineered for the most severe coastal environments and meet the strictest HUD requirements. Zone 3 homes include heavy-duty anchoring systems, impact-resistant features, and construction techniques specifically designed for 110-mph wind zones.
Important: Because Zone 3 homes require specialized engineering and materials, not all manufacturers produce them, and availability may be limited. However, a Zone 3 home can be placed in any zone (3, 2, or 1), making it a smart choice if you may relocate in the future or want maximum wind protection.
Ready to find a wind zone-compliant home? Get pre-approved today and browse our inventory of Zone 1, Zone 2, and Zone 3 certified manufactured homes. Our team will help match you with homes that meet your location's exact requirements.
Related Link: How to Take Your Mobile Home Off the Grid

Can I Trust the Wind Zone Rating for My Home?
HUD takes the responsibility of ensuring the safety of manufactured homes seriously. This department must protect the inhabitants, not the manufacturers, and is especially true when considering the poor record of older mobile homes. As such, the agency has devised several tests that a home must pass before it is approved. Only the agencies authorized by HUD can perform these tests to approve the home. They include the following:
-
An agency for the design of the load-bearing components
-
An in-plant inspection of the manufacturing process and home
-
The manufacturer itself
-
And a state supervisor
Clearly, with all these guidelines, tests, inspections, and regulations you can rest assured that your home is designed specifically for the wind zone you plan to live in.
Every manufactured home must display a HUD Certification Label (a red metal plate) on the exterior of each transportable section. This label confirms that the home was built in compliance with federal standards, including the appropriate wind zone rating. Never purchase a manufactured home without verifying these labels are present and intact.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Wind Zone Home
Anyone looking to purchase a home wants assurances that their investment is sound; even when purchasing a mobile home. You hope the place you choose to live provides you with security, stability, and peace. Knowing that manufacturers have built your home specifically for the wind zone you live in will give you just that.
Understanding wind zones isn't just about following regulations; it's about protecting your family, your investment, and your peace of mind. Whether you're buying your first manufactured home or relocating an existing one, always verify that the home's wind zone rating matches or exceeds your location's requirements.
At Home Nation, we're committed to helping you navigate wind zone requirements and find a home that's not only beautiful and affordable but also safe and compliant for your specific location. Our team of experts can answer your questions about wind zones, help verify your area's classification, and guide you to homes that meet every requirement.
Start your search today:
-
Browse our inventory of wind zone-certified homes
-
Speak with a Home Nation specialist about your area's requirements
See what other Home Nation buyers have to say about us! Check out reviews here.






